Learn How Colors Work in Media Editing with Hue, Saturation, and Value
Have you ever played around with your media editor's Hue, Saturation, and Value settings? These are the key elements of the HSV color model, which is an alternative to the more commonly used RGB (Red, Green, and Blue) model. But why should you care? Well, understanding HSV lets you master color manipulation and enhance your media editing skills. Furthermore, this article will simplify HSV and guide you on using it effectively in your media editor.
Part 1. What are Hue, Saturation, and Value?
We see color when light passes through something clear or bounces off an object. It happens because our eyes pick up certain light waves. Colors comprise three things: Hue, Saturation, and Value.
Hue
This refers to the color, such as red or blue. It's the first thing we say when describing a color. Light encompasses three fundamental hues: red, green, and blue. These hues function together in electrical devices such as televisions and computer monitors via red, green, and blue phosphors.
Saturation
This describes how bright and powerful a color is. Less brightness equals less saturation. It gets less radiant when we add white or black. Saturation, often known as “intensity” or “chroma,” describes how much a color stands out. Consider a color wheel: the color becomes less visible as you get closer to the center. No color stands out in the middle, which we term desaturated hues.
Value
This is how light or dark a color is. It's like saying how bright or dark the color looks. In a color wheel, it displays the overall brightness or intensity of the color. Consider the color wheel a circle, with the value represented by a straight line running through the center, indicating the range from light to dark.
Part 2. Differences in Hue, Saturation, and Value
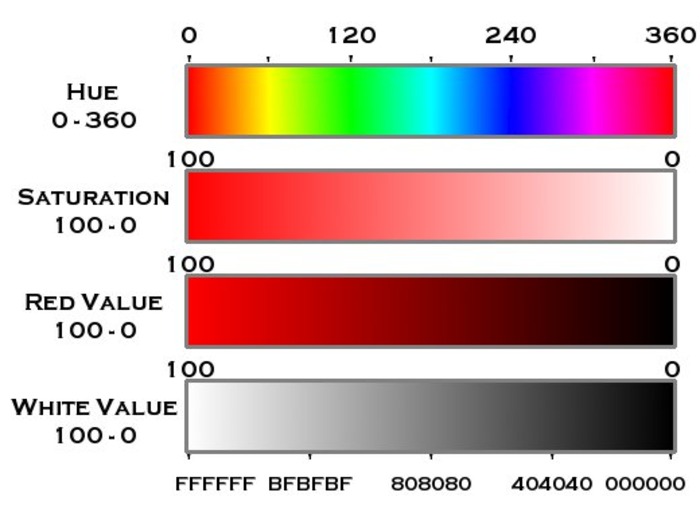
Hue displays the color type on a wheel (0 to 360 degrees) in the HSV color standard. Saturation and Value are percentages (0% to 100%), with Saturation representing the intensity of a color and Value showing its brightness. White has no distinct hue, but black lacks both color and brightness. The brightness of gray ranges from 0 to 100. This table simplifies HSV values, allowing us to better grasp colors by their Hue, Saturation, and Value.
| Color | Hue(degrees) | Saturation(%) | Value(%) |
| Red | 0 | 100 | 100 |
| Yellow | 60 | 100 | 100 |
| Green | 120 | 100 | 100 |
| Cyan | 180 | 100 | 100 |
| Blue | 240 | 100 | 100 |
| Magenta | 300 | 100 | 100 |
| White | – | 0 | 100 |
| Black | – | 0 | 0 |
| Grey | – | 0 | (0-100) |
Part 3. Best Hue, Saturation, and Value settings for Video
The ideal HSV settings for your video depend on the specific scenario you're filming. Below, we'll provide five examples of video scenarios to illustrate how adjusting your Hue, Saturation, and Value settings can enhance and improve your video content.
Cinematic
To make your video appear more like a movie, use less vibrant colors with a hint of red and orange. Keep the colors not too bright for a classy look, and make sure there's a decent mix of light and dark to capture the cinematic ambiance without losing details.
◆ Hue: 30-40 degrees (warm tones, leaning towards red and orange).
◆ Saturation: 70-80% (moderate saturation for sophistication).
◆ Value: 50-60% (balanced contrast without losing details).
City
Give city scenes a cool and captivating vibe by using blues and grays. Play with the colors to create a balance of modern and classic. For the lights and streets, keep the colors vibrant but natural. Ensure the bright and gloomy areas are balanced appropriately for a lively city look.
◆ Hue: 200-220 degrees (cooler tones, leaning towards blues and grays).
◆ Saturation: 60-70% (moderate saturation for a natural feel).
◆ Value: (balance between well-lit areas and shadows).
Nature
Highlight the greens for plants and the browns for the earthy sections of nature sceneries to make them stand out. Boost the hues, especially during bright seasons such as spring or fall. Adjust the brightness to catch natural light to see details in bright and gloomy areas. This will certainly make your nature video glow.
◆ Hue: Hue: 80-120 degrees (natural tones, emphasizing greens and browns).
◆ Saturation: Saturation: 80-90% (amplified saturation for vibrant colors).
◆ Value: Value: 50-70% (adjust brightness based on lighting conditions).
Bright Day
Capture the warmth of a bright day by using warmer tones that trend towards yellows and oranges. By adjusting your hues in this manner, you can give your video a warm, sunny appeal. Keep things balanced and natural by not going overboard with color saturation. Increase the brightness to match the intensity of the sunshine while ensuring that details are visible in both bright and shady locations. This method guarantees that your video seems warm, lively, and true to a sunny day.
◆ Hue: 40-60 degrees (warm tones, leaning towards yellows and oranges).
◆ Saturation: 60-70% (moderate saturation for a natural look).
◆ Value: (slightly increased brightness for a sunlit appearance).
Summer
Use bright and sunny tones in your video to capture the essence of summer—think yellows, oranges, and light blues. Change the settings to match your summer spot, whether it's a beach, park, or outdoor event. Increase the saturation to capture the vibrant hues of summer, particularly in flowers and blue sky. Increase the brightness to mimic the intensity of the light while preserving depth in shadows. This method assures that your video emanates a cheerful and sun-soaked summer vibe.
◆ Hue: 40-60 degrees (warm tones, favoring yellows, oranges, and light blues).
◆ Saturation: 80-90% (amplified saturation for vibrant summer colors).
◆ Value: (enhanced brightness for a lively summer feel).
Part 4. How to Adjust Hue, Saturation, and Value Using Video Converter Ultimate
Video Converter Ultimate is your top choice for enhancing videos with ease. It supports over 1000 formats and handles multiple tasks at once. Beyond basic conversion, it's a complete media toolbox featuring 3D creation, color correction, watermark removal, and more. Imagine adjusting your video's Hue, Saturation, and Value while instantly viewing the results! Furthermore, whether you're an experienced editor or just getting started, this tool puts simplicity and power at your fingertips.
Step 1. To acquire the program, simply click the link below. Double-click the downloaded file to install it. Once installed, run the program.
Free DownloadFor Windows 7 or laterSecure Download
Free DownloadFor MacOS 10.7 or laterSecure Download
Step 2. Click on the Toolbox icon, scroll down, and choose the Color Correction tool. Import the video you wish to edit by clicking the Add sign in the center.
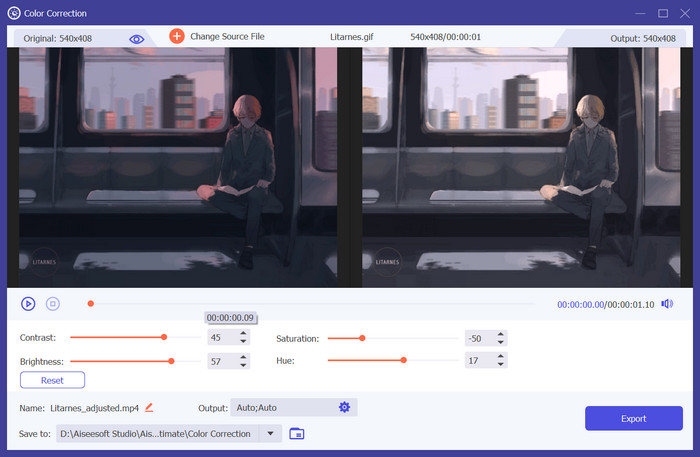
Step 3. You'll find both the original video and the output within the program. Edit your Hue, Saturation, and Value below. Once satisfied, click the Export button located in the lower right corner.
Further Reading:
How to Change the Hue of Video? Exploring the Creative Possibilities
Add Saturation to Video: Incredible Tips and Tricks Here
Part 5. FAQs About Hue, Saturation, and Value
What is the difference between HSV and RGB?
HSV simplifies color comparison in picture processing by differentiating color from brightness. RGB, however, is defined by describing the proportions of red, green, and blue in a single number.
Is it possible to convert an HSV color to RGB?
Yes, it is possible to convert a hue, saturation, and value (HSV) color code to RGB (red, green,and blue) and vice versa.
Where is HSV applied?
HSV is a color model used in various fields. Video editors use it to adjust video colors, enhance hues, and create specific moods.
Conclusion
We hope you learned something new about HSV and its use in video editing. We recommend utilizing a reliable application like Video Converter Ultimate to acquire the best Hue and Saturation settings. It will make your editing easier and faster and ensure your video content retains quality.



 Video Converter Ultimate
Video Converter Ultimate Screen Recorder
Screen Recorder